Importance of Customer Due Diligence for AML Compliance in Singapore
Money laundering is a serious financial crime that threatens the stability of economies worldwide. In Singapore, it is no different. As a major financial hub in the Asia-Pacific region, Singapore is particularly vulnerable to money laundering activities. In response, Singapore has implemented stringent regulations and guidelines to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
One such important measure is customer due diligence (CDD), which refers to the process of verifying the identity and assessing the risk of customers before establishing a business relationship with them. CDD helps businesses to identify and manage the risk of financial crime, including money laundering and terrorist financing.
In recent years, Singapore has made significant progress in combating money laundering and terrorist financing. However, with the constantly evolving nature of financial crimes, it is critical that businesses remain vigilant and adapt to new threats. In the following sections, we will discuss the legal framework for CDD in Singapore, the importance of CDD for businesses and best practices for conducting effective CDD.
The Legal Framework for CDD in Singapore
In Singapore, CDD is a legal requirement under various regulations and guidelines. The key laws governing CDD include the Corruption, Drug Trafficking and Other Serious Crimes (Confiscation of Benefits) Act, the Terrorism (Suppression of Financing) Act, and the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) guidelines.
Under these laws, financial institutions, including banks, insurance companies, and new-age fintech firms, must conduct CDD on their customers before establishing a business relationship. CDD aims to identify and assess the risk of money laundering and terrorist financing activities.
The MAS guidelines provide detailed requirements for conducting CDD, including identifying and verifying customer identity and beneficial ownership, as well as ongoing monitoring of customer activity. The guidelines also set out the different levels of CDD that financial institutions must undertake, depending on the level of risk associated with the customer.
The three levels of CDD are simplified, basic, and enhanced. Simplified CDD applies to low-risk customers, such as those who are regulated by the MAS or government entities. Basic CDD applies to customers who are deemed to have a medium risk of money laundering or terrorist financing, while enhanced CDD applies to high-risk customers, such as politically exposed persons (PEPs) or those with complex ownership structures.
Financial institutions are required to apply the appropriate level of CDD based on the customer's risk assessment. They must also keep detailed records of their CDD processes and report any suspicious transactions to the relevant authorities.
Read More: Importance of CDD at Singapore Digital Banks for AML Compliance
The Importance of CDD for Financial Institutions in Singapore
Conducting thorough CDD is not just a legal requirement but also an essential business practice for businesses operating in Singapore.
- One of the key benefits of conducting thorough CDD is protecting against reputational risk. Money laundering and terrorist financing activities are serious crimes that can tarnish a business's reputation and damage its relationships with customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders. By conducting thorough CDD, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to preventing financial crime and maintaining high ethical standards.
- Another benefit of CDD is avoiding regulatory fines and penalties. Failure to conduct appropriate CDD can result in significant financial penalties, regulatory action, and even criminal prosecution. Businesses that do not comply with CDD requirements may also face restrictions on their business activities or be subject to increased scrutiny by regulatory authorities.
- Maintaining customer trust is also an important consideration for businesses. Customers expect their personal and financial information to be protected from fraud and theft. By conducting CDD, businesses can help prevent fraudulent activities, protect customer data, and build customer trust.
Steps in CDD
The key steps in conducting CDD include identifying customers, verifying their identity and beneficial ownership, and assessing their risk level. To identify customers, businesses should obtain and review relevant documentation, such as identity cards or passports, and other records, such as business registration documents.
To verify customer identity and beneficial ownership, businesses may use various methods, including electronic identity verification, physical inspections, and interviews with customers. Finally, companies must assess the risk level of their customers to determine the appropriate level of CDD that should be applied. A typical CDD workflow is given below.
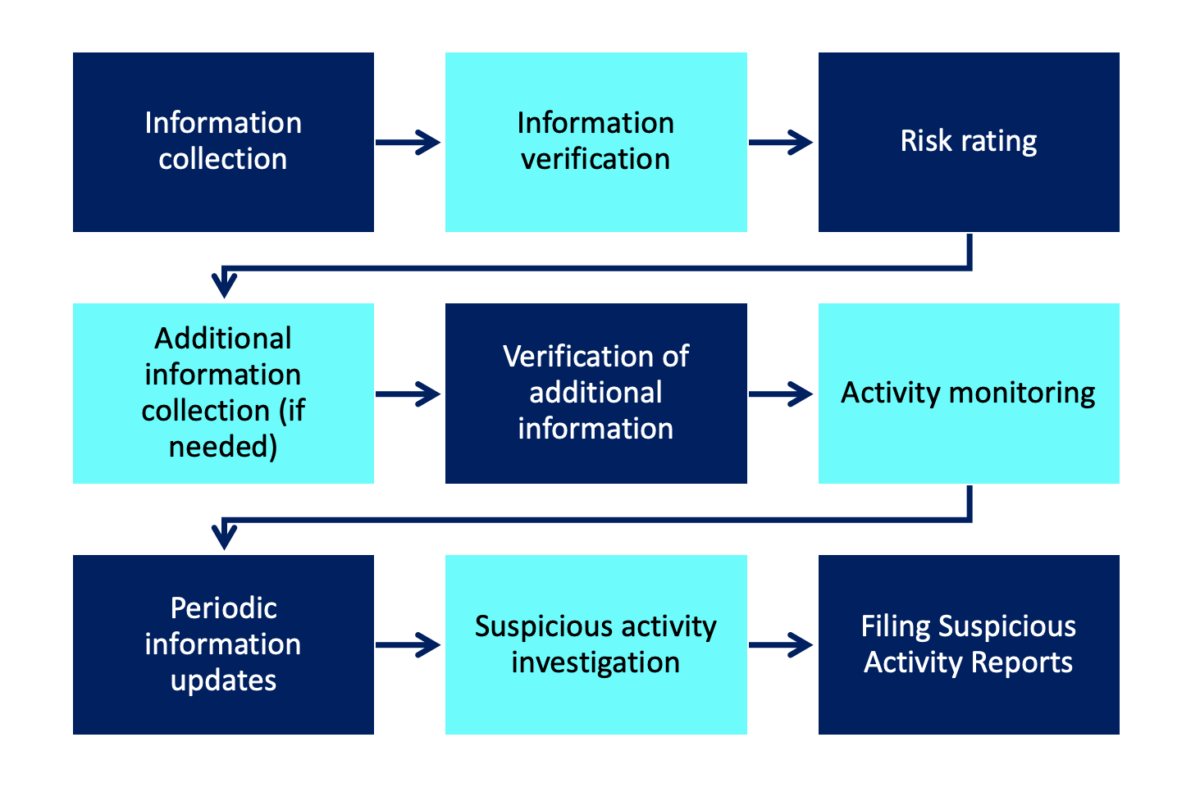
Best Practices for Conducting Effective CDD in Singapore
To conduct effective CDD in Singapore, businesses should follow a set of best practices to comply with regulatory requirements and protect themselves against financial crime. These best practices include:
- Conduct Ongoing Monitoring: Businesses should regularly monitor customer activity to detect suspicious transactions and ensure they remain compliant with regulatory requirements. This involves monitoring transactions and customer behaviour continuously and investigating any red flags that may arise.
- Train Staff on CDD Procedures: To ensure that CDD procedures are consistently and accurately followed, businesses should provide training to all relevant staff members. This training should cover the importance of CDD, the applicable regulations and guidelines, and the specific procedures that need to be followed.
- Maintain Accurate Records: Accurate record-keeping is essential for effective CDD. Businesses should keep customer information records, including identification documents and transaction records. These records should be regularly reviewed and updated as necessary.
- Conduct Regular Risk Assessments: Regular risk assessments help businesses identify potential risk areas and adjust their CDD procedures accordingly. This involves assessing the risk associated with different customers and transactions and adjusting the level of CDD accordingly.
- Keep Up to Date with Regulatory Changes: Regulations and guidelines related to CDD are regularly updated. To comply with the latest regulatory requirements, businesses should stay current with these changes.
By following these best practices, businesses can conduct effective CDD and protect themselves against financial crime. This, in turn, helps to maintain the integrity of the financial system and promote a stable and secure business environment in Singapore.
The Role of Technology in CDD
Technology plays a critical role in facilitating effective CDD in Singapore. Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms can significantly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of CDD processes. One company that offers advanced CDD solutions is Tookitaki. Its CDD solutions leverage cutting-edge technology and advanced analytics to help businesses automate their CDD processes and detect potential financial crime.
Tookitaki's solutions include:
- Smart Screening: This solution helps businesses to screen prospects and customers at the time of onboarding and on an ongoing basis.
- Transaction Monitoring: An essential process in ongoing monitoring, our transaction monitoring solution enables financial institutions to monitor customer transactions to identify any potential red flags. The solution is powered by a growing database of typologies sourced from Tookitaki’s AFC Ecosystem.
- Dynamic Risk Scoring: This solution uses advanced analytics to assign risk scores to prospects and customers based on various factors.
By leveraging Tookitaki’s technology in their CDD processes, financial institutions can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of their procedures and detect potential financial crime more effectively. This helps maintain the financial system's integrity and promotes a secure and stable business environment in Singapore.
Protect Your Business and Reputation: Prioritise CDD in Singapore
In conclusion, CDD is crucial in preventing money laundering and terrorist financing in Singapore. The legal framework and regulations surrounding CDD, coupled with the risks posed by financial crime, make it essential for businesses to prioritize CDD in their operations.
Tookitaki offers advanced CDD solutions that leverage technology to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of CDD processes. By utilizing these solutions, businesses can ensure compliance with regulations, reduce the risk of financial crime, and maintain the trust of their customers. We urge financial institutions in Singapore to prioritize CDD in their operations and take advantage of the advanced CDD solutions offered by Tookitaki. Book a demo today to learn how Tookitaki can help your business protect itself against financial crime and maintain a secure and stable business environment in Singapore.
Anti-Financial Crime Compliance with Tookitaki?




