The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) is Singapore’s central bank and the city state’s financial regulator. Established in 1971, MAS acts as the Singapore government’s banker. MAS regulates the country’s money, banking, insurance and securities businesses and administers its currency issuance.
MAS works with the financial industry to develop Singapore as a dynamic international financial centre. MAS’s responsibilities also include the prevention of money laundering and terrorism financing in the country. It formulates broad policies and programmes for financial institutions to curb financial crimes and protect the Singapore economy.
According to the official website, MAS’s vision is “to promote sustained non-inflationary economic growth, and a sound and progressive financial centre.” It lists integrity, commitment, enterprise and teamwork as its values.
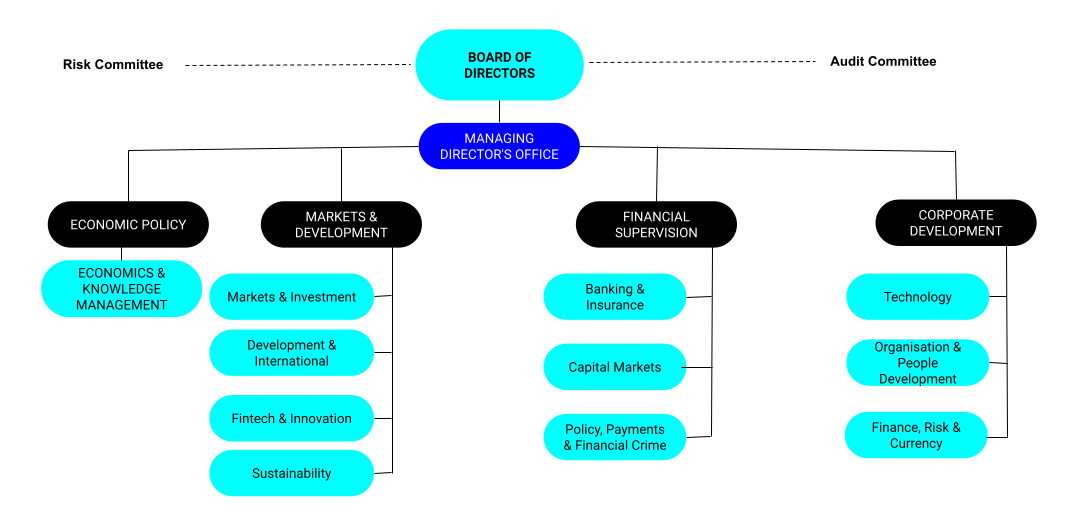
Monetary Authority of Singapore Organisation Chart
MAS is governed by a Board of Directors and chaired by the Minister for Finance of the country. The Board of Directors is responsible for the policy and general administration of the affairs and business of MAS and informs the Government of the regulatory, supervisory and monetary policies of the MAS. The Chairman of the Board is appointed by the President on the recommendation of the Cabinet. Tharman Shanmugaratnam currently serves as the Chairman of MAS, while Ravi Menon serves as its Managing Director.
The organisation structure of MAS at a broader level is depicted in the graphic below.
What does the Monetary Authority of Singapore do?
MAS has the following functions according to the official website:
- To act as the central bank of Singapore, including the conduct of monetary policy, the issuance of currency, the oversight of payment systems and serving as banker to and financial agent of the Government.
- To conduct integrated supervision of financial services and financial stability surveillance.
- To manage the official foreign reserves of Singapore
- To develop Singapore as an international financial centre
Central Bank
As central bank, has the following responsibilities:
- Promoting sustained, non-inflationary economic growth through the conduct of monetary policy and close macroeconomic surveillance and analysis.
- Managing Singapore’s exchange rate, official foreign reserves, and liquidity in the banking sector.
- Serving as a financial agent and banker to the government with facilities to deposit money and to transact with international bodies such as the World Bank.
Integrated Financial Supervisor
MAS’s role as a financial supervisor includes the following duties:
- Fostering a sound financial services sector through its prudential oversight of all financial institutions including banks, insurers, capital market intermediaries, financial advisors, and stock exchanges.
- Ensuring well-functioning financial markets, sound conduct, and investor education.
Growth Promoter
As a growth enabler and promoter, MAS has the following functions:
- Working with the financial industry to promote Singapore as a dynamic international financial centre.
- Facilitating the development of infrastructure, adoption of technology, and upgrading of skills in the financial industry.
What makes the Monetary Authority of Singapore unique among central banks
While MAS’s role and responsibilities as a central bank are broadly similar to those of its counterparts across the globe, there are certain characteristics that make it unique. We will explore those in the below section.
Monetary policy
Since 1981, monetary policy in Singapore has centred on the management of the exchange rate. MAS conducts its monetary policy by managing the trade-weighted exchange rate index (TWI) in contrast to peers who rely on short-term interest rates or monetary aggregates. This strategy was adopted taking in mind the country’s small and open economic profile and the fact that the majority of consumer goods are imported.
Exchange rate policy
MAS sets the value of the Singapore dollar by aggregating the value of some of its trading partner currencies. Based on its secret currency “basket”, it sets the optimal value for the home currency.
Fintech policy
MAS has been very expressive about its ambition to transform Singapore into a “Fintech Nation”. It encourages and promotes the implementation of financial technology to spur economic growth. It envisions Singapore as a regional Fintech hub with various initiatives intended at developing a large talent pool, creating an open architecture economy, strengthening cybersecurity measures and fostering an atmosphere of innovation.
Policy updates
While its counterparts may need several meetings and produce numerous updates to their monetary policy in a year, Singapore’s simple economic structure permits MAS to cut down its meetings to two times in a year — April and October. MAS announces changes to its exchange rate policy after these meetings, if any, so that these meetings are closely watched by the business community in the country.
AML policy
Being a prominent member of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), MAS devots special attention to its anti-money laundering (AML) and countering the funding of terrorism (CFT) policies. It frequently issues special AML and CFT notices and guidelines to all regulated financial firms. They include requirements to submit suspicious transaction reports (STRs) and to have proper Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures.
Recent developments
In October 2021, MAS announced that it is introducing “a digital platform and enabling regulatory framework” to allow financial institutions to share information on customers and transactions to prevent money laundering.
The new platform, named “Collaborative Sharing of ML/TF Information & Cases” (COSMIC) will be the first centralised platform where information is shared in a structured format that allows for seamless integration with data analytics tools, according to MAS.
MAS expects to roll out the COSMIC platform in the first half of 2023. It will initially focus on three key financial crime risks in commercial banking, namely, abuse of shell companies, misuse of trade finance for illicit purposes and proliferation financing.
How can Tookitaki help financial institutions in Singapore?
A fast-growing Regtech company, Tookitaki has developed an end-to-end AML compliance platform called the Anti-Money Laundering Suite (AMLS). It offers multiple solutions catering to the core AML activities such as transaction monitoring, name screening, transaction screening and customer risk scoring. Powered by advanced machine learning, AMLS addresses the market needs and provides an effective and scalable AML compliance solution.
To learn more about our AML solution and its unique features that help financial institutions in Singapore to enhance their risk-based AML compliance programmes, book a meeting with one of our experts here.
Anti-Financial Crime Compliance with Tookitaki?


